A look at greenhouse temperature, calculated plant temperature and dew point temperature and the reasons for high condensation risk.
Back to: How to avoid condensation in the greenhouse
The graph in Figure 1 shows a day at Millbeck Nursery following implementation of our first set of climate control settings as described in How to achieve good humidity control with minimum energy use
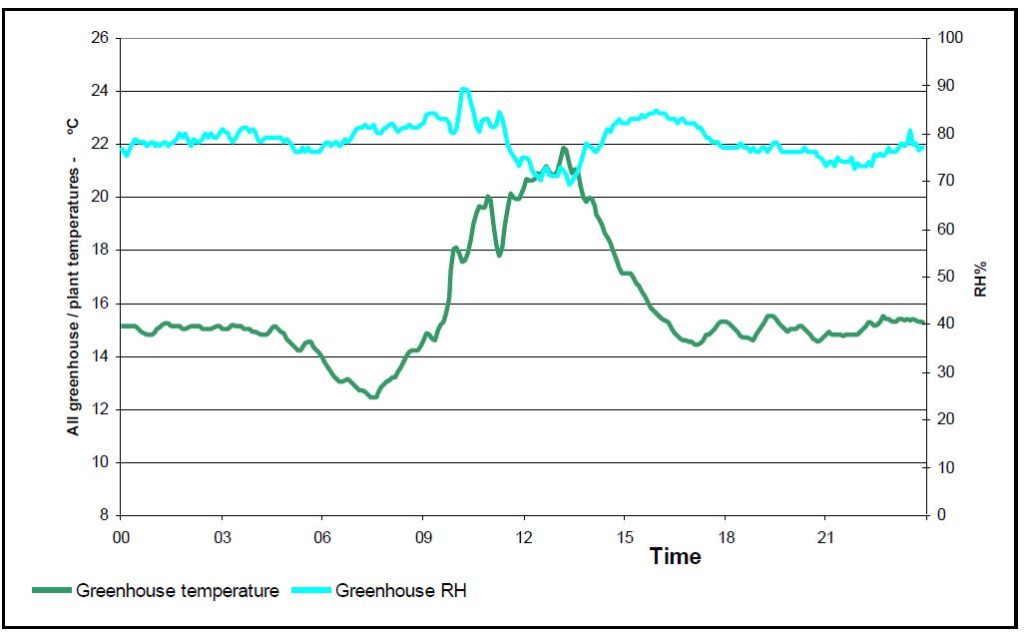
At a first glance the greenhouse climate looks acceptable, however if we add some additional information potential problems are revealed.
The graph in Figure 2 shows the same period, but in addition to the greenhouse temperature (in green) two other lines have been added:
- The calculated plant temperature (in pink) and;
- The dew point temperature of the greenhouse air (in brown).
These lines show that the calculated plant temperature was the same as the dew point temperature between 10:00 and 10:30; so at this time the risk of condensation on the plants was extremely high.
Whilst we can’t say conclusively that condensation occurred at this time, this graph tells us that the risks were high.
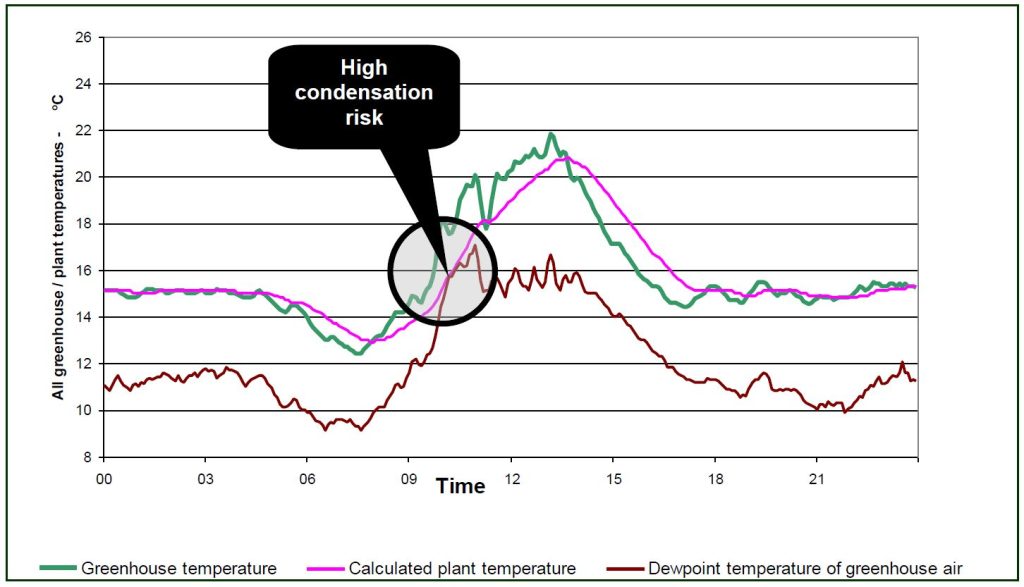
Why was the condensation risk high?
- High RH; so the moisture holding capacity of the greenhouse air was very close to saturation.
- The plants were yet to warm up following the low temperature ‘Drop’ treatment.
So what are the solutions?
1. Give the plant more time to warm-up before allowing the differential between the heating and ventilation temperatures to increase.
To implement this option, introduce higher ventilation temperatures more gradually. This effectively delays the start of the daytime heating and ventilation set-points (i.e. Period 3; see How to achieve good humidity control with minimum energy use).
This strategy avoids the use of any additional heat.
2. Lower the RH during the warm-up period by using more heat.
To implement this option an increase in pipe heat during the transition period is needed so energy costs will be higher.